What is Computer Programming? । Basics, Types & Notes PDF : In this post you are learn about the basic of programming languages,types and definition etc.
What is Program?
A program is a set of instructions written in a programming language that tells a computer how to perform specific tasks. Programs can be used for a variety of tasks, including basic calculations, sorting, online banking, data analytics, and artificial intelligence.
What is Instructions?
Instructions are the commands(LINE) in the program that will instruct C compiler to perform specific tasks or actions. Whenever we write a C instruction, we are telling C compiler to do a task for us
What is Programming?
Programming is the process of writing instructions, or code, for a computer to follow in order to solve a problem. Programmers use languages like Python, JavaScript, and C++ to write, test, and maintain code. In Simple words, Programming is the process of writing instructions to tell a computer how to perform a task.
What is a Programming Language?
- A programming language is a set of rules and syntax that allows a programmer to write instructions for a computer to follow.
- A programming language is a set of instructions that programmers use to tell computers what to do. Programming languages are essential because computers can’t understand English.
- Examples : Python, Java, C++, JavaScript.
How Does It Work?
- Code : The instructions or commands written by a programmer in a programming language are called code.
- Compiler/Interpreter : These are programs that translate the code into machine language (the language computers understand).
Types of Programming Languages
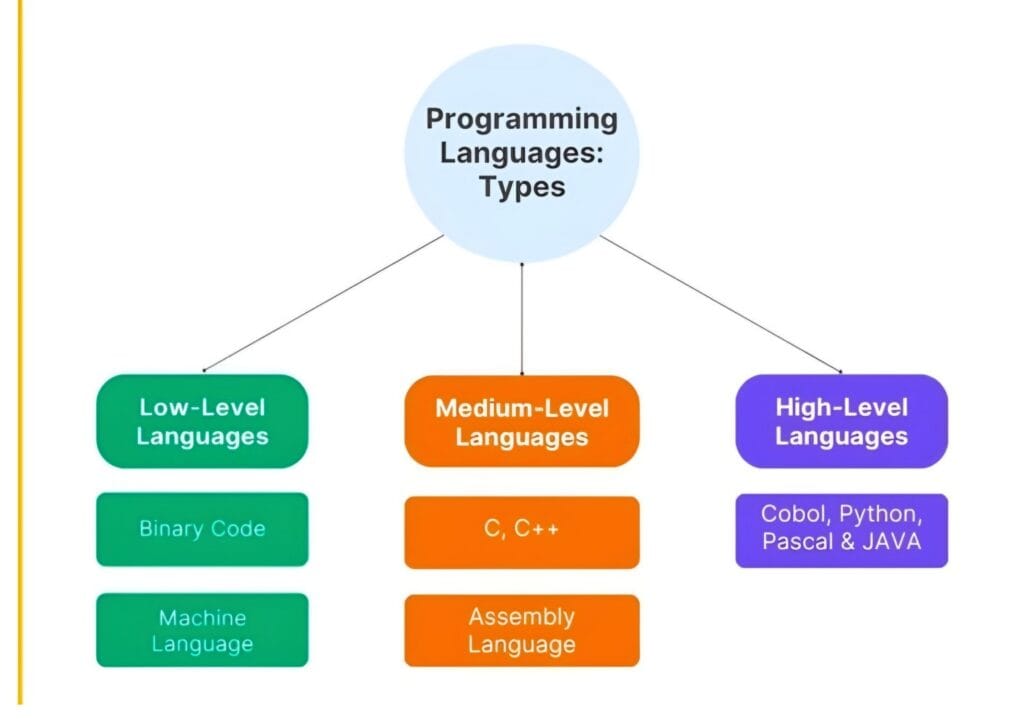
There are there types of programming languages:
- Low-level programming language
- High-level programming language
- Middle-level programming language
Low-level programming language
Low-level language is machine-dependent (0s and 1s) programming language. Low-level languages are closer to machine code and hardware. They are harder for humans to read but give the programmer more control over the computer’s hardware.
The processor runs low- level programs directly without the need of a compiler or interpreter, so the programs written in low-level language can be run very fast.
Low-level language is further divided into two parts :
- Machine Language
- Assembly Language
Machine Language
Machine language is a type of low-level programming language. It is also called as machine code or object code. Machine language is easier to read because it is normally displayed in binary or hexadecimal form (base 16) form. It does not require a translator to convert the programs because computers directly understand the machine language programs.
The advantage of machine language is that it helps the programmer to execute the programs faster than the high-level programming language.
- The most basic language, consisting of binary (0s and 1s). The computer directly understands it.
- Example: 101101010100 (this is not readable for humans).
Assembly Language
Assembly language (ASM) is also a type of low-level programming language that is designed for specific processors. It represents the set of instructions in a symbolic and human-understandable form. It uses an assembler to convert the assembly language to machine language.
The advantage of assembly language is that it requires less memory and less execution time to execute a program.
- Slightly easier than machine language, it uses short words (called mnemonics) instead of numbers.
- Example: MOV AX, 01 (move the value 1 into register AX).
- Assembly requires a special program called an assembler to convert it into machine code.
High-level programming language
High-level programming language (HLL) is designed for developing user-friendly software programs and websites. This programming language requires a compiler or interpreter to translate the program into machine language (execute the program).
High-level programming language includes Python, Java, JavaScript, PHP, C#, C++, Objective C, Cobol, Perl, Pascal, LISP, FORTRAN, and Swift programming language.
A high-level language is further divided into three parts :
- Procedural Oriented programming language
- Object-Oriented Programming language
- Natural language
Procedural Oriented programming language
Procedural Oriented Programming (POP) language is derived from structured programming and based upon the procedure call concept. It divides a program into small procedures called routines or functions.
Procedural Oriented programming language is used by a software programmer to create a program that can be accomplished by using a programming editor like IDE, Adobe Dreamweaver, or Microsoft Visual Studio.
The advantage of POP language is that it helps programmers to easily track the program flow and code can be reused in different parts of the program.
Example : C, FORTRAN, Basic, Pascal, etc.
Object-Oriented Programming language
Object-Oriented Programming (OOP) language is based upon the objects. In this programming language, programs are divided into small parts called objects. It is used to implement real-world entities like inheritance, polymorphism, abstraction, etc in the program to makes the program resusable, efficient, and easy-to-use.
The main advantage of object-oriented programming is that OOP is faster and easier to execute, maintain, modify, as well as debug.
Example : C++, Java, Python, C#, etc.
Natural language
Natural language is a part of human languages such as English, Russian, German, and Japanese. It is used by machines to understand, manipulate, and interpret human’s language. It is used by developers to perform tasks such as translation, automatic summarization, Named Entity Recognition (NER), relationship extraction, and topic segmentation.
The main advantage of natural language is that it helps users to ask questions in any subject and directly respond within seconds.
Middle-level programming language
Middle-level programming language lies between the low-level programming language and high-level programming language. It is also known as the intermediate programming language and pseudo-language.
A middle-level programming language’s advantages are that it supports the features of high-level programming, it is a user-friendly language, and closely related to machine language and human language.
Example : C, C++, language
Pseudocode
Pseudocode is a way of planning an algorithm using simple, human-readable language. It is not meant to be executed by a computer, but it helps in understanding and designing the logic of a program before writing actual code. Pseudocode focuses on the steps and logic, without worrying about the syntax of a specific programming language.
Example : Let’s write pseudocode for finding the largest of two numbers :
Start
Input number1
Input number2
If number1 is greater than number2 then
Output “number1 is the largest”
Else
Output “number2 is the largest”
End
Algorithm
An algorithm is a step-by-step procedure or a set of rules to solve a problem. It is more formal than pseudocode and often includes more details on how the solution is to be implemented. An algorithm can be written in various forms like pseudocode, structured text, or even as a flowchart.
Start
Input two numbers: number1 and number2
If number1 > number2
Output “number1 is the largest”
Else
Output “number2 is the largest”
End
Example : Algorithm for finding the largest of two numbers :
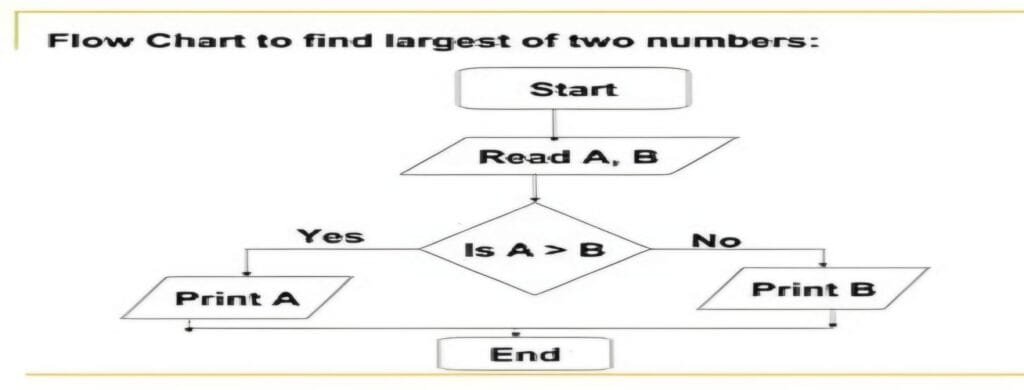
Flowchart
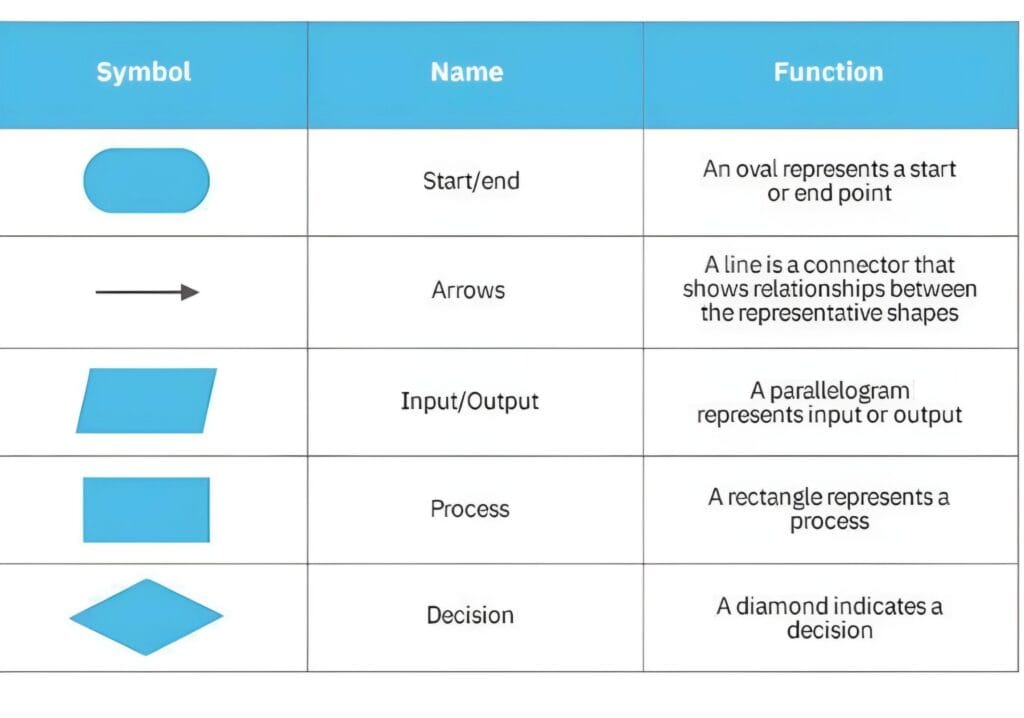
A flowchart is a diagram that represents the flow of logic or a process. It uses various shapes (rectangles, diamonds, ovals, etc.) to represent different steps or decisions in a process. Flowcharts are a visual way to design and represent an algorithm or process.
Example : Here is a flowchart for finding the largest of two numbers :
Basics of Computer Programming Notes PDF Download
Click on the link given below to download PDF of Basics of Computer Programming Notes.
| Heading | Links |
|---|---|
| Basics of Computer Programming Notes Download Link | Click Here |
| Join WhatsApp Group Link | Click Here |
| Join Telegram Group Link | Click_Here |
View More
- राजस्थान रीट लेवल 1 सिलेबस और एग्जाम पैटर्न जारी, यहां से PDF डाउनलोड करे
- राजस्थान रीट लेवल 2 सिलेबस और एग्जाम पैटर्न जारी, यहां से PDF डाउनलोड करे
- राजस्थान ग्राम विकास अधिकारी सिलेबस जारी, यहां से PDF डाउनलोड करे
- IDBI Bank ESO Vacancy 2024
- ITBP Telecom Vacancy 2024
- MGSU Bikaner Syllabus PDF Download
- MLSU Udaipur Syllabus PDF Download
- MDSU AJMER BSc BEd Old Question Papers Download
- MDSU AJMER BA Semester Syllabus PDF Download
- MDSU AJMER BSc Semester Syllabus PDF Download
- VMOU Kota Syllabus PDF Download
- Rajasthan University Jaipur Syllabus PDF Download 2024-25
- राजस्थान जमाबंदी नकल कैसे देखें?


